The David Sinclair research team at Harvard Medical School addressed this issue by conducting a clinical study in overweight or obese adults over the age of 45 to evaluate the effect of NMN (niacinamide mononucleotide) on improving weight, cholesterol and blood pressure.
David Sinclair’s team at Harvard Medical School published an important study in 2023 in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
As the number of overweight and obese people continues to increase globally, so do obesity-related health problems.
Research content
Participants: 30 overweight or obese older adults over the age of 45 were recruited to participate in the study.
Intervention: Participants were given 2,000 mg of NMN daily for 28 days.

Control group setting: A placebo group also set up to ensure the accuracy of the study results.
Research result
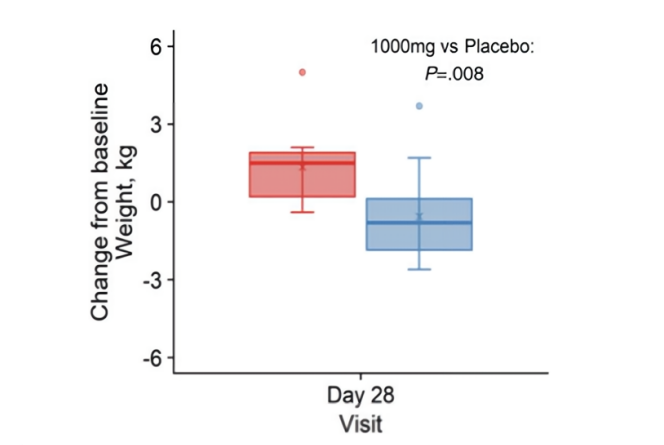
Weight loss: Participants who received the NMN intervention lost more than 6 pounds of weight compared to participants who did not receive niacinamide mononucleotide.
This suggests that niacinamide mononucleotide has the potential to boost metabolism and reduce body weight.
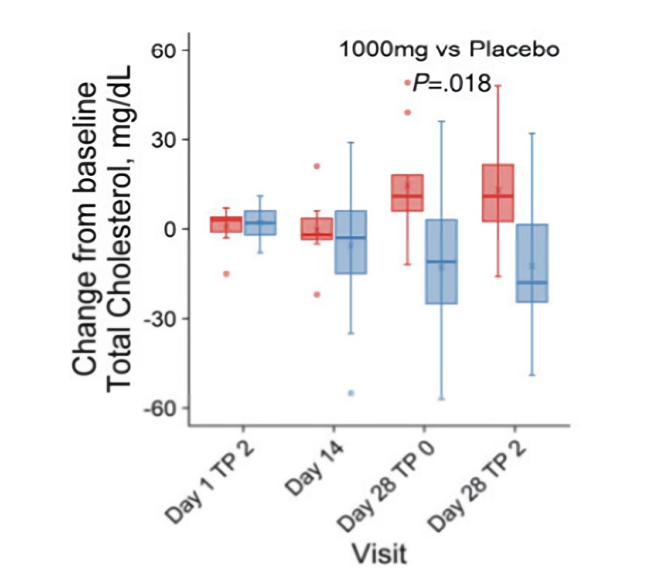
Cholesterol reduction: Studies have also found that NMN can lower total cholesterol levels, specifically low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), known as the “bad cholesterol.”
This helps reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
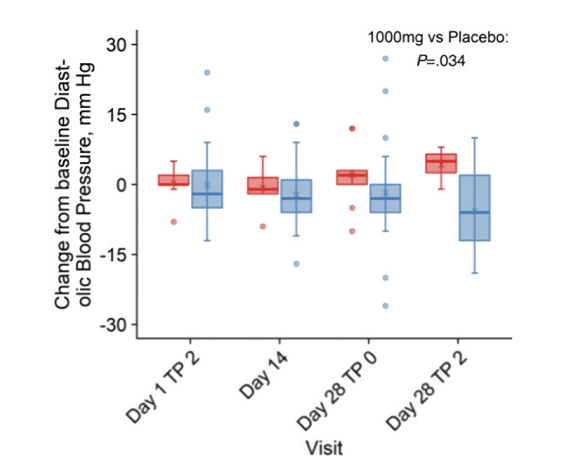
Lower blood pressure: niacinamide mononucleotide reduces diastolic blood pressure, indicating that it helps to lower blood pressure.
Diastolic blood pressure is one of the key factors in high blood pressure, so this finding has important implications for improving cardiovascular health.
significance
This study provides strong evidence for the role of NMN in improving the health of overweight and obese adults.
By reducing weight and lowering cholesterol and blood pressure, niacinamide mononucleotide may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease associated with obesity.
The study also further validated the benefits of niacinamide mononucleotide in promoting metabolic function.




