What is glutathione?
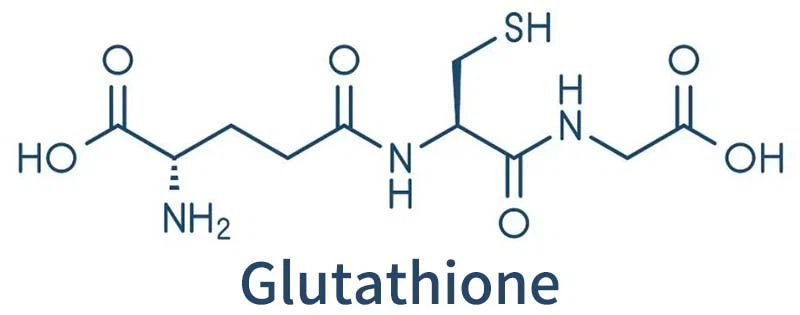
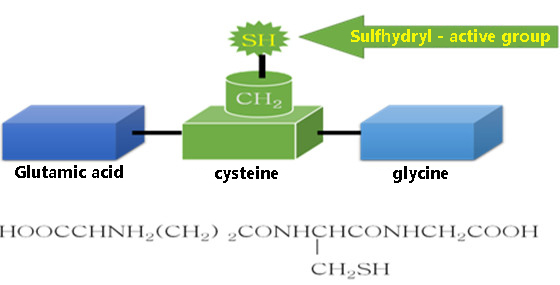
glutathione (r-glutamyl cysteingl +glycine,GSH) is a tripeptide consisting of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine.
It’s present in almost every cell of the body.
GSH can help maintain the normal function of the immune system, and has an antioxidant effect and integrated detoxification effect, the sulfhydryl group on cysteine is its active group (often abbreviated as G-SH), easy to combine with some drugs (such as paracetamol), toxins (such as free radicals, iodoacetic acid, mustard gas, lead, mercury, arsenic and other heavy metals), and has an integrated detoxification effect.
Glutathione has a broad spectrum detoxification effect, which can not only be used as drugs, but also as the base material of functional foods, and is widely used in functional foods such as delaying aging, enhancing immunity, and anti-tumor.
GSH is a tripeptide composed of glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine, containing sulfhydryl groups, which has antioxidant and integrated detoxification effects.
The thiol group on cysteine is the active group of glutathione (so GSH is often abbreviated as G-SH), which is easy to combine with some drugs (such as paracetamol) and toxins (such as free radicals, iodoacetic acid, mustard gas, lead, mercury, arsenic and other heavy metals), and has an integrated detoxification effect.
Therefore, glutathione (especially GSH in liver cells) can participate in biological transformation, thereby transforming harmful poisons in the body into harmless substances and excreting out of the body.
Glutathione also helps maintain normal immune system function.
Glutathione can reduced (G-SH) and oxidized (G-S-S-G) in two forms, and the reduced glutathione the majority under physiological conditions.
GSH reductase catalyzes tautomerism between the two types. The coenzyme of this enzyme provides NADPH for pentose phosphate bypass metabolism.
Glutathione function
Excessive free radicals produced by the body’s metabolism will damage the biofilm, invade the macromolecules of life, accelerate the aging of the body, and induce the production of tumors or atherosclerosis. Glutathione plays an important role in the biochemical defense system of human body and has many physiological functions.
Its main physiological role is to remove free radicals in the human body, as an important antioxidant in the body, to protect many proteins and enzymes and other molecules in sulfhydryl.
The structure of GSH contains an active sulfhydryl -SH, which easily dehydrogenated by oxidation, and this specific structure makes it the main free radical scavenger in the body.
For example, when a small amount of H2O2 produced in the cell, GSH reduces H2O2 to H2O under the action of GSH peroxidase, and itself oxidized to GSSG, which receives H to reduced to GSH under the action of glutathione reductase present in the liver and red blood cells, so that the free radical scavenging reaction in the body can continued.
Glutathione can not only eliminate free radicals in the human body, but also improve human immunity.
GSH is healthy and anti-aging, and has a greater effect on the cells that slow down in older people than in younger ones.
Glutathione can also protect hemoglobin from hydrogen peroxide oxidation, free radicals and other oxidation, so that it can continue to perform normal oxygen transport capacity.
Part of the hemoglobin in the red blood cells under the action of oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide, in which the bivalent iron oxidized to trivalent iron, so that the hemoglobin transformed into methemoglobin, thus losing the oxygen carrying capacity.
Reduced glutathione can not only directly combine with oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide to form water and oxidized glutathione, but also reduce methemoglobin to hemoglobin.
GSH is abundant in human red blood cells, which is of great significance to protect the sulfhydryl group of proteins on the red blood cell membrane in a reduced state and prevent hemolysis.
Glutathione protects the -SH group in the enzyme molecule, which conducive to the play of the enzyme activity, and can restore the activity function of the -SH group in the enzyme molecule that has destroyed, so that the enzyme can resume the activity.
GSH also inhibits the fatty liver caused by ethanol.
Glutathione has a strong protective effect on the symptoms of leukopenia caused by radiation and radiopharmaceutics.
GSH can combined with toxic compounds, heavy metal ions or carcinogens that enter the human body, and promote their excretion from the body, playing a role of neutralization and detoxification.

The effect of glutathione combined with vitamin C
Vitamin C is also an important antioxidant in the body.
Because vitamin C can reversibly hydrogenated or dehydrogenated, vitamin C plays an important role in many REDOX reactions in the body.
For example, the active group of many enzymes is sulfhydryl (-SH), and vitamin C can maintain -SH in a reducing state and maintain enzyme activity;
Vitamin C can transform oxidized glutathione into reduced glutathione (GSH) and reduce hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produced by body metabolism.
Vitamin C also protects vitamins A, E and certain B vitamins from oxidation.
Glutathione, when used in combination with vitamin C, can improve its efficacy.
Glutathione action
- (1) Detoxification
- (2) Radiation sickness and radiation protection
- (3) Liver protection
- (4) Anti-allergy
- (5) Ameliorate the course and symptoms of certain diseases
- (6) Beauty and skin care
- (7) Increased vision and eye disease
- (8) Anti-aging effect