Analysis of the combination of sodium fructose diphosphate and citicoline in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in the elderly
Effect of sodium fructose diphosphate (FDP) combined with citicoline (CDPC) in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in middle and severe elderly.
The results of the study indicate that FDP in combination with CDPC shows higher efficacy and better prognosis in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in the elderly compared to CDPC alone.
Part 1 Research background
Ischemic encephalopathy, especially moderate and severe ischemic encephalopathy in the elderly, is a common disease of the central nervous system, with a high disability rate and fatality rate.

With age, the vascular system of the elderly gradually ages, and the incidence of atherosclerosis increases, resulting in an increased risk of narrowing or blocking of the blood vessels of the brain.
When the blood supply of the brain vessel cannot meet the metabolic needs of the brain tissue, ischemic encephalopathy will be caused, manifested by sudden neurological deficits, such as hemiplegia, aphasia, and consciousness disorders.
The treatment for ischemic encephalopathy mainly includes drug therapy, surgery and rehabilitation.
Drug therapy is an important means of early intervention, aiming to reduce brain injury and improve the quality of life and prognosis of patients by improving cerebrovascular circulation, protecting neurons and promoting nerve regeneration.
Fructose diphosphate (FDP) is an intracellular high energy phosphate product, which can improve cell metabolism and increase cell energy supply.
In neurological diseases, FDP can reduce nerve cell damage and promote the recovery of nerve function. Citicoline (CDPC) is a neurotransmitter precursor that promotes phospholipid synthesis, enhances cell membrane stability, and promotes the repair and regeneration of damaged neurons.
Both have shown certain efficacy in the treatment of nervous system diseases.
As for the effect of FDP combined with CDPC in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in the elderly, there is still insufficient research and evidence support.
The purpose of this study was to explore the value of FDP combined with CDPC in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in middle and severe elderly people, in order to provide a new choice and basis for clinical treatment.
Through a randomized controlled trial, this study will evaluate the efficacy and safety of FDP in combination with CDPC in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in the elderly and provide scientific guidance for clinical practice.
Part 2 Materials and methods
Grouping and treatment methods:
In this study, 60 patients with ischemic encephalopathy in the elderly were randomly divided into two groups. The observation group was treated with FDP and CDPC, while the control group was treated with CDPC only.
Curative effect evaluation:
The evaluation criteria of efficacy included that the neurological symptoms and signs disappeared within 5 days as a significant effect, disappeared within 10 days as an effective, more than 10 days did not disappear as an ineffective.
Neurobehavioral function was evaluated using the Fugl-Meyer score.
Part 3 Research results
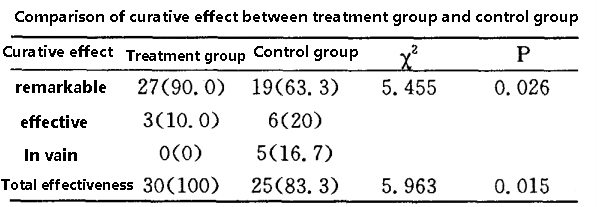
The apparent efficiency and total response rate of the treatment group (combined application group) were significantly higher than those of the control group (CDPC only group).
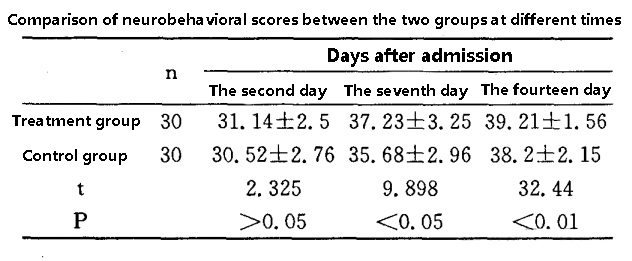
On days 7 and 14, neurobehavioral scores were significantly higher in the treatment group than in the control group.
Clinical efficacy:
Comparison of neurobehavioral scores:
Part 4 Research and discussion
In this study, we observed that the combination of sodium fructose diphosphate (FDP) and citicoline (CDPC) in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in moderate to severe elderly patients has a higher efficacy and better prognosis than CDPC alone.
This finding has important implications for clinical treatment, especially in the elderly, a population with a high incidence.
We need to recognize that ischemic encephalopathy is a complex disease, its pathogenesis involves many aspects, including cerebrovascular circulation disorders, nerve cell damage and so on.
A single therapeutic drug may not fully cover their treatment needs.
FDP, as an intracellular high energy phosphate product, can improve cell metabolism and increase cell energy supply, thereby helping to reduce nerve cell damage.
CDPC can promote phospholipid synthesis, enhance cell membrane stability, and promote the repair and regeneration of damaged neurons.
The mechanisms of action of the two drugs are complementary, and combined use may be able to more fully cover the therapeutic needs of ischemic encephalopathy.
The results of this study show that the combined application of FDP and CDPC has a good effect on improving clinical symptoms and signs and promoting the recovery of neurological function.
This result may be related to the synergistic effect of the two drugs. In combination, the two drugs may be able to enhance each other’s efficacy, leading to faster improvements in patients’ conditions.
This study also observed a greater improvement in neurobehavioral scores in the combination group, which further confirms the advantages of the combination in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy.
We should also note the limitations of this study.
Due to the limited sample size, there may be some bias in the results of this study.
Larger studies are needed in the future to further validate the conclusions of this study.
Possible drug interactions were not investigated in depth in this study.
In practical application, the doctor needs to choose the appropriate treatment plan according to the specific situation of the patient, considering various factors comprehensively.
We need to recognize that the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy is a long-term process, which requires comprehensive consideration of drug therapy, surgical treatment, rehabilitation treatment and other aspects.
In this study, we only looked at the effects of medication.
Future studies could further explore the combined effect of the combination in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy, as well as synergies with other therapeutic approaches.
In summary, the combination of FDP and CDPC in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in the middle and severe elderly is an effective treatment, with high efficacy and good prognosis.
More studies are needed to further validate this conclusion and explore its specific application in clinical practice.

Part 5 Research conclusion
A randomized controlled trial was conducted to investigate the effect of sodium fructose diphosphate (FDP) combined with citicoline (CDPC) in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in moderate and severe elderly.
Compared with CDPC alone, the combination of FDP and CDPC showed higher efficacy and better prognosis in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in moderate to severe elderly people.
Specifically, the significant efficiency and total effective rate of the combined application group were significantly higher than those of the control group, indicating that the combined application of FDP and CDPC can improve the clinical symptoms and signs of patients more effectively.
In terms of neurobehavioral scores, the combined application group had significantly higher scores than the control group on day 7 and day 14, indicating that the combined application could promote the recovery of neurological function more quickly.
No obvious adverse reactions observed during the study, indicating that the combination of FDP and CDPC has good safety and tolerability.
In summary, this study concluded that the combined application of FDP and CDPC in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in moderate and severe elderly people is an effective treatment scheme, which can significantly improve the efficacy and prognosis.
This conclusion provides a new choice and basis for clinical treatment, and is worthy of further promotion and application in clinical practice.
Due to the limited sample size of this study, larger studies needed in the future to further verify this conclusion.
References:
[1] DONG F.Combination of sodium fructose diphosphate and citicoline in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in the elderly [J]. Chinese Medicine for Disability and Disability,2009,17(04):38-39.
Review content
1, Research background and importance
Disease characteristics: Ischemic encephalopathy in the elderly is a common clinical disease of the central nervous system, with a high rate of disability and mortality.
Treatment needs: Drug therapy is an important means of early intervention, aiming to reduce brain damage and improve the quality of life and prognosis of patients.
2, Mechanism of drug action
Fructose diphosphate (FDP) : Function: improve cell metabolism, increase cell energy supply.
Function in nervous system: reduce nerve cell damage and promote the recovery of nerve function.
Citicoline (CDPC) : Function: promote phospholipid synthesis, enhance cell membrane stability.
Role in the nervous system: promotes the repair and regeneration of damaged neurons.
3, Research methods and results
Methods: Subjects: 60 patients with moderate to severe elderly ischemic encephalopathy.
Group: Randomly divided into observation group (FDP combined with CDPC) and control group (CDPC alone).
Results: Efficacy: The apparent efficiency and total effective rate of the combined treatment group (observation group) were significantly higher than those of the control group.
Neurobehavioral scores: On days 7 and 14, the combined group had significantly higher neurobehavioral scores than the control group.
4, Research conclusions
Efficacy advantage: The combination of FDP and CDPC has shown higher efficacy and better prognosis in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in moderate and severe elderly people.
Mechanism of action: The mechanisms of action of the two drugs are complementary, and the combined application may more fully cover the treatment needs of ischemic encephalopathy.
5, Comments and Prospects
Significant efficacy: According to the study results, the significant efficiency and total effective rate of the combined application group were significantly higher than those of the control group, indicating that the combined application of FDP and CDPC has significant advantages in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in the elderly.
Safety considerations: Although the study did not mention specific information about adverse drug reactions, in practical applications, doctors need to consider the specific situation of patients and drug interactions and other factors to ensure the safety of treatment.
Limitations of the study: The sample size of this study limited, and larger studies needed to further verify the conclusions in the future.
Further research on drug interactions also needed.
Application prospect: The combined application of FDP and CDPC in the treatment of ischemic encephalopathy in the elderly shows therapeutic advantages, which provides a new choice and basis for clinical treatment.
Future studies could further explore the synergies of this treatment regimen with other therapeutic approaches, as well as specific applications in clinical practice.

