Beta Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is a derivative of vitamin B3 that has recently gained significant attention for its potential health and anti-aging effects.
As a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a crucial molecule involved in energy metabolism and cell repair, NMN may support these biological processes when supplemented. This article explores the current understanding of NMN-what it is, its reported benefits, sources, safety considerations, and future research directions.
Understanding Beta Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN)
NMN is a nucleoside molecule structurally similar to nicotinamide riboside, another derivative of vitamin B3. The human body has innate capacity to produce small amounts of NMN, particularly in the liver, kidneys and muscles.

As a precursor, NMN can convert into NAD+ through several enzymatic steps to enhance energy metabolism. NAD+ is an important coenzyme involved in many vital cellular processes including energy production, DNA repair, cell signaling pathways and more.
Declining NAD+ levels over time may contribute to age-related decline across body systems. As a key NAD+ precursor, NMN supplementation aims to raise NAD+ levels to support healthy cellular function.
Reported Health Benefits Of NMN
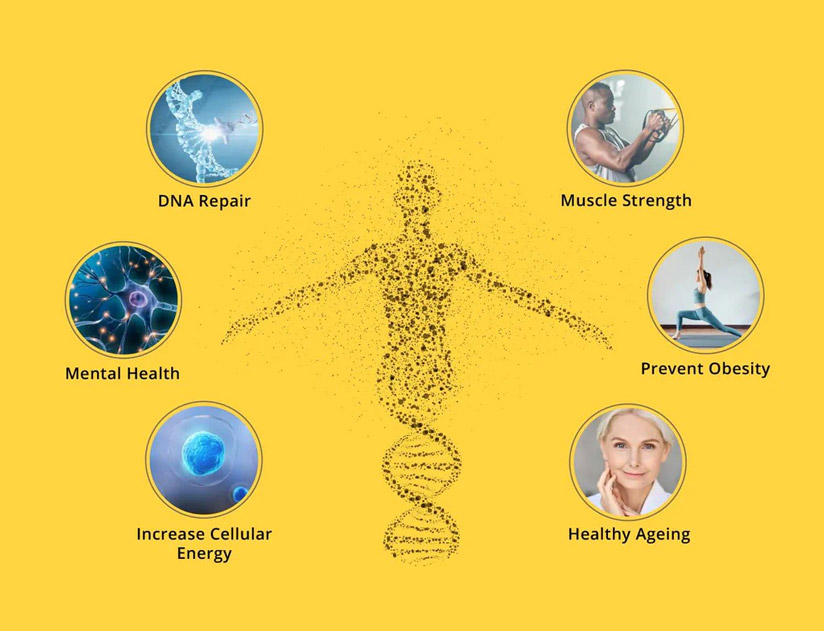
Based on recent studies in animals and some human trials, NMN supplementation may offer several health benefits:
Anti-Aging Effects
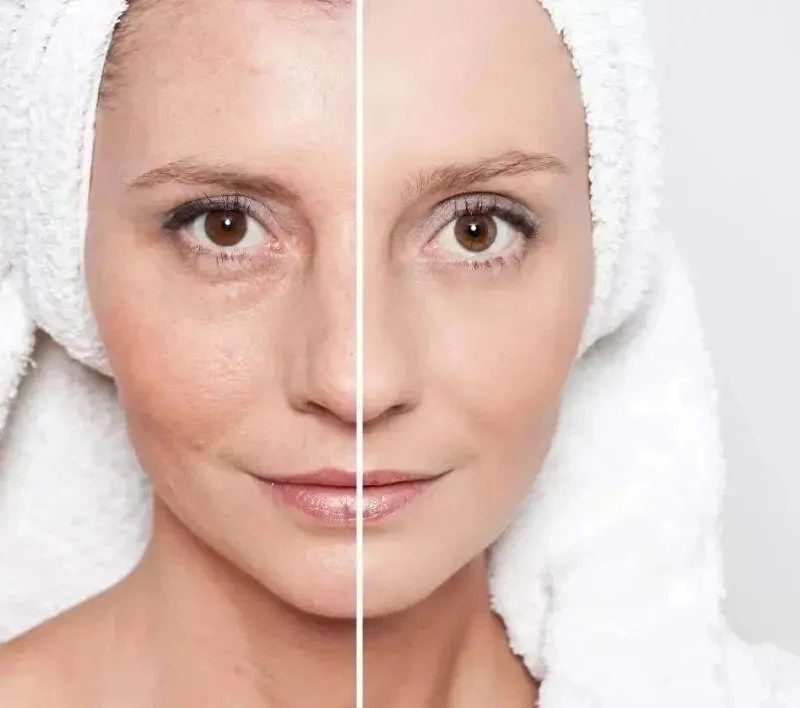
Loss of NAD+ has associated with aging. Some research shows NMN may increase NAD+ levels and mitigate age-associated decline in mice including vision loss, weight gain, diabetes and neurodegeneration though human evidence still limited. Small human trials found increased artery flow and blood vessel generation indicating cardiovascular benefits as well.
Metabolic Support
By boosting NAD+ levels, NMN may also optimize energy metabolism pathways like glucose breakdown and mitochondrial function that tend to show age-related disruption. This can translate into improved muscle and liver health in aging mice. Enhanced metabolism could also promote weight control.
Cellular Repair
NAD+ is required for DNA damage repair via protein interactions. Some studies demonstrate Beta Nicotinamide Mononucleotide administration assists in vascular tissue, bone marrow and neural repair in rodent models indicating broader regenerative capacity. EnhancedDNA repair may also contribute to longer lifespans.
While these results seem promising, larger scale, controlled human trials over longer periods are still necessary to conclusively confirm anti-aging and disease-preventing impacts. Most current evidence stems from animal research or small, short-duration human studies calling for additional rigorous investigation. Still, the theoretical mechanisms align with NMN’s biological roles suggesting therapeutic potential warrants further exploration.
Sources Of NMN
The human body can produce NMN internally through various biosynthetic pathways. However, internal NMN production diminishes with age. Some foods also naturally contain trace amounts of NMN, usually in microgram quantities. Richer sources include:
- Broccoli – 0.25-1.12 micrograms per gram
- Avocados – 2.23-2.28 micrograms per gram
- Raw cabbage – 0.14 micrograms per gram
- Tomatoes – 0.24 micrograms per gram
Given limited dietary sources, NMN supplements may offer a more viable route to obtain higher concentrations likely required for experiential benefits. Various NMN supplements are now available over-the-counter in capsule or powder formulations. These synthetically manufactured to provide NMN in larger doses than food sources, often 100-500 milligram per capsule.
As research continues demonstrating optimal dosing ranges for humans remain unclear. Consultation with a health practitioner advised to guide personalized supplement regimens according to individual health status.

Safety And Considerations
Despite emerging research on efficacy, Beta Nicotinamide Mononucleotide supplements have not yet undergone approval and regulation processes from government bodies. Hence, quality control mechanisms in manufacturing remain unclear. Choosing reputable suppliers is advised.
Limited side effect profiles are currently available given small sample sizes in trials. Mild effects like headaches and light fatigue have sporadically occurred but data remains limited.
NMN supplementation also carries some specific considerations:
- Effects may depend on baseline health status. Younger, healthy adults with robust NAD+ conversion may show limited gains compared to elderly or those with comorbidities.
- Optimal dosages are currently unestablished in humans. Most studies administered 100-500 milligrams daily. Higher doses may increase side effect likelihood. Gradually increasing intake while monitoring tolerance is sensible.
- Drug or health condition interactions remain unknown. NMN may alter medication absorption or exacerbate underlying health conditions. Professional advice is critical for those on current medications or with chronic diseases.
Current Research And Future Directions
As an active arena of scientific inquiry, Beta Nicotinamide Mononucleotide research continues evolving. Ongoing work involves elucidating mechanisms of transport and conversion to optimize bioavailability. Researchers also continue investigating anti-aging therapeutic potential and prevention of neurodegeneration, diabetes and other age-onset conditions. Upcoming clinical trials registered across Asia, Europe and North America signal continued research momentum.
These cumulative research efforts may solidify understanding of NMN pharmacological kinetics and clinical applications. With further supportive evidence, approved indications for managing age-related chronic diseases or health maintenance can be defined. Standardized quality controls around manufacturing may also emerge to ensure supplement integrity.
In summary, ongoing scientific interest in NMN stems from its critical involvement in fundamental biological processes that wane across the lifespan. Though still an emerging nutraceutical compound, early research suggests NMN supplementation may help recapture lost NAD+ levels to alleviate age-related physiological decline. However, considerable work remains to fully elucidate its long-term impacts in larger human populations. Patients are advised to consult healthcare providers before use and adhere to safe dosing guidelines once available. While not a miracle cure, NMN may someday offer feasible means to promote healthy aging.



