What is the use of CoQ10? Do middle-aged and elderly people really need to supplement?
Coenzyme Q10, which is widely concerned in the field of nutrition and medicine, not only plays a vital role in maintaining the health of human cells, but also shows its unique charm in anti-aging, improving immunity and protecting cardiovascular disease.
For middle-aged and elderly people, because of the gradual decline of physical function, coenzyme Q10 supplement seems to become a potential way of health care.
Do these people really need to supplement coQ10?
Before answering this question, we must first understand the function of coenzyme Q10.
What is the use of Coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10, a natural substance known as the “spark of life”, is deep in the mitochondria of our human cells and is an essential element for cellular energy production.
It not only has a deep historical accumulation in the field of medical research, but also shows its irreplaceable and diversified value in maintaining and promoting human health.
Coq10 is a powerful support for our immune system.
As the primary defense line of the human body, the immune system always stands at the forefront of resisting the invasion of external viruses, bacteria and other pathogens.
In this critical physiological process, coenzyme Q10 plays a pivotal role.
With its unique biological properties, Coenzyme Q10 injects a powerful impetus into the robust operation of the immune system.
Immune cells, such as T lymphocytes and macrophages, which are the core components of the immune system, are responsible for recognizing and eliminating pathogens from the body.
Studies have confirmed that coenzyme Q10 can effectively enhance the proliferation and functional activity of these immune cells, making them more courageous and efficient in the fight against pathogens.
Further, CoQ10 can significantly enhance the body’s resistance to viruses and bacteria.
This benefit is mainly due to the excellent antioxidant capacity of Coenzyme Q10.
When pathogens invade our bodies, they are accompanied by the production of a large number of free radicals.
These free bases are destructive and they impair the normal function of immune cells, thereby reducing our body’s resistance.
Coq10 acts as a highly effective free radical scavenger, quickly neutralizing these harmful molecules and protecting immune cells from damage.
The presence of coenzyme Q10 undoubtedly builds a solid defense line for us to help us better resist the invasion of viruses and bacteria.
Coq10 also showed significant anti-inflammatory effects.
Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to pathogens, but an excessive inflammatory response can lead to tissue damage and various diseases.
Coq10 can inhibit the production of inflammatory factors, thereby reducing the inflammatory response and providing our body with an additional layer of protection, which has important implications in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory diseases.
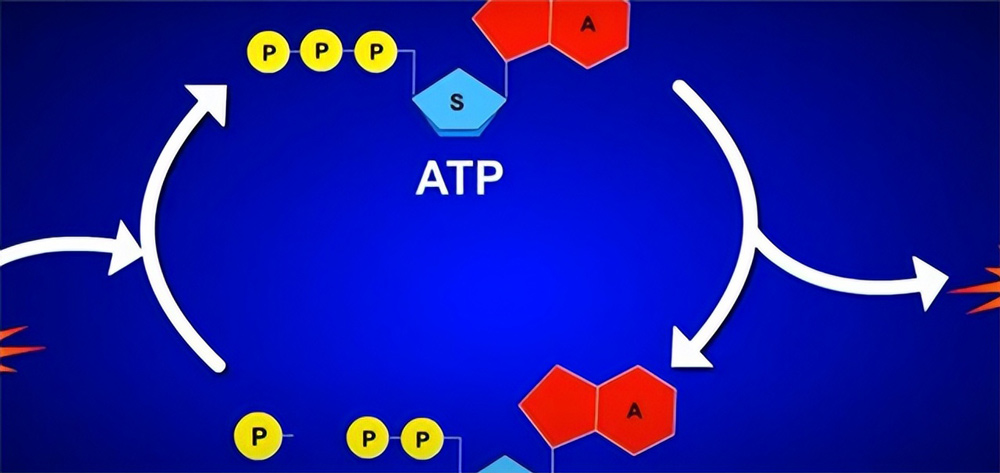
Another highlight of CoQ10 is its key role in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, as the core component of this chain, CoQ10 is directly involved in the synthesis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) process.
ATP is the primary source of energy for cells and drives almost all cellular activities.
In the electron transport chain, Coenzyme Q10 acts as a highly efficient electron carrier, accurately transporting electrons from complexes I and II to Complex III.
The energy released during this transfer process is used to phosphorylate ADP (adenosine diphosphate) into ATP, which provides the cell with a constant stream of energy.
The smooth operation of cellular energy production is essential for sustaining life activities, and the lack of coQ10 will directly affect the supply of energy, which in turn will interfere with the normal function of multiple organ systems.
However, studies have pointed out that by timely supplementing coenzyme Q10, we can effectively maintain the normal operation of cell energy metabolism, and then delay the pace of aging.

In particular, it is worth mentioning that in terms of heart health, coenzyme Q10 also shows its unique protective effect.
In the study, published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, researchers recruited a group of patients with heart failure and put them through a clinical trial of coenzyme Q10.
The study design was a randomized, double-blind controlled trial in which one group of patients received a coQ10 supplement and the other group received a placebo.
The results showed that left ventricular ejection fraction, coenzyme Q10 levels, mitochondrial respiratory chain activity, and ATP production were significantly improved in this group of patients, while there was no significant change in the placebo group, and NT-proBNP levels also showed a downward trend, indicating a reduced cardiac burden.
This finding suggests that coenzyme Q10 may provide more energy support to the heart, improving symptoms in patients with heart failure.
Further analysis also found that coenzyme Q10 can effectively neutralize harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the body, reducing the damage of oxidative stress to the heart.
This antioxidant effect is essential for maintaining heart health, as oxidative stress is one of the important factors that contribute to heart disease.
In particular, coQ10 inhibits the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL).
LDL, the so-called “bad cholesterol,” is prone to forming atherosclerotic plaques when oxidized, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Research data show that the supplementation of coenzyme Q10 significantly reduces the oxidation level of LDL, which helps to slow the process of atherosclerosis and reduce the probability of cardiovascular adverse events.

In addition to the many benefits mentioned above, coenzyme Q10 may have an adjunct role in cancer treatment.
By boosting immune function and mitigating the side effects of chemotherapy,
CoQ10 is expected to bring better treatment outcomes and quality of life for cancer patients.
In summary, Coenzyme Q10, with its diverse health benefits and key role in energy production,
is an essential nutrient for maintaining human health.
Whether it is the support of the immune system, the play of anti-inflammatory effects,
or the contribution of heart health protection, coenzyme Q10 has shown its irreplaceable value.
This is also why many middle-aged and elderly people are keen to supplement coenzyme Q10, so for middle-aged and elderly groups,
Do you really need a CoQ10 supplement?

Do middle-aged and elderly people need to supplement coQ10?
Although coenzyme Q10 can bring many benefits to the human body,
not all middle-aged and elderly people need additional coenzyme Q10,
and its actual demand is closely related to individual health status and lifestyle.
Coq10 supplementation is particularly important for middle-aged and elderly people who suffer from chronic diseases or specific health problems.
Cardiovascular disease is a common disease in middle-aged and elderly people,
and studies have shown that coQ10 can improve cardiac muscle function and reduce blood pressure levels in patients with hypertension.
Middle-aged and elderly people suffering from circulatory problems such as heart disease and high blood pressure can consider appropriate supplementation of coenzyme Q10.
The role of CoQ10 in promoting energy metabolism makes it helpful for middle-aged and elderly people with diabetes,
especially those who need to control their blood sugar through medication.

On the other hand, those middle-aged and elderly people who are in good health and have no obvious diseases may not need to deliberately supplement coQ10.
Coq10 levels do decline with age, but if you can get enough through a balanced diet,
then additional supplements may not be necessary.
Excessive intake of coQ10 may also sometimes cause some side effects, such as stomach upset, headache and so on.
For middle-aged and elderly people who often participate in physical exercise and maintain good living habits,
their physical functions are often maintained better.
There may still be a relatively stable balance between their naturally occurring coQ10 capacity and their daily needs.
In such cases, it is usually not recommended that they blindly pursue additional coQ10 supplementation unless they have been evaluated in detail by a professional physician and have confirmed that there is a clear need for CoQ10 supplementation.

For middle-aged and elderly people considering coenzyme Q10 supplementation,
it is wise to proceed under the guidance of a professional doctor.
The doctor will give individual recommendations based on the specific circumstances of each patient,
such as past medical history, current medication, and the body’s absorption and response to coQ10.
It is important to emphasize that coQ10 should be considered as an adjunct therapy rather than a panacea.
Before deciding on a supplement, it is important to fully communicate with your doctor to ensure that you choose the best health plan for you.
Although we have some basic understanding of the function of coenzyme Q10 and the suitable population,
we still need to master some scientific and reasonable methods to supplement coenzyme Q10.

How to supplement Coenzyme Q10 scientifically and reasonably?
Supplementing Coenzyme Q10 is not done overnight, it requires scientific and reasonable planning and methods, as follows:
Choosing the right Coenzyme Q10 product is crucial,
and there are a wide variety of Coenzyme Q10 products on the market, including oxidized Coenzyme Q10 and reduced Coenzyme Q10,
the latter of which is more bioavailable and easier to be absorbed by the body.
The dosage form of the product can also affect its effect,
such as the softgel form may be more suitable for the absorption of oily substances.
When purchasing, you should choose a well-known brand, pay attention to the purity,
stability and related quality certification of the product, to ensure the safety and reliability of the selected product.

Coenzyme Q10 is a fat-soluble antioxidant found in a variety of foods.
Foods rich in coenzyme Q10 include eggs, milk, broccoli, etc. These foods can not only provide coenzyme Q10, but also contain rich other nutrients to help maintain good health.
It is also important to note how the drug interacts with coQ10.
Because Coenzyme Q10 fat-soluble, its absorption needs to rely on the fat in the food,
it recommended to ingestion with fatty foods, such as nuts, fish, etc., can promote its better absorption.
It should noted that some drugs such as cholesterol-lowering drugs may affect the level of coQ10, if you taking such drugs, you need to supplement coQ10 under the guidance of a doctor to avoid adverse drug interactions.
Continuous monitoring and timely adjustment of the supplement amount is also an important part of ensuring the scientific and reasonable supplement of coenzyme Q10.
Supplementing coQ10 is not a once-and-for-all, but a dynamically regulated process.
Regular detection of relevant biochemical indicators, such as blood lipid, blood sugar and blood concentration of coenzyme Q10,
is helpful to monitor the supplement effect, and adjust the supplement dose according to the actual situation.
This procedure also needs to carried out under the guidance of a professional physician to ensure safety and effectiveness.

At the same time, it cannot neglected to cultivate a healthy lifestyle,
which as an auxiliary means can significantly enhance the production of endogenous coQ10 and enhance the effect of external supplementation.
Specifically, healthy habits such as quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake,
maintaining a balanced diet, and engaging in regular moderate exercise are all key to maintaining coQ10 levels.
Harmful substances in tobacco damage the antioxidant system within cells and reduce the activity of coenzyme Q10.
Quitting smoking can significantly reduce this damage, allowing the body’s coenzyme Q10 to do its job better.
Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with the normal function of the liver, which is the main organ that synthesizes coQ10.
Moderate or avoidance of alcohol can ensure liver health and maintain normal levels of coQ10;
Various nutrients rich in food are important raw materials for the synthesis of coenzyme Q10.
By eating enough nutrients such as protein, fat, vitamins and minerals,
we can provide the body with the material base needed to synthesize Coenzyme Q10;
Exercise can promote blood circulation and speed up metabolism, thereby improving the body’s absorption and utilization efficiency of nutrients.
Exercise can also enhance the body’s antioxidant capacity,
reduce free radical damage to cells, and thereby protect the activity of coenzyme Q10.
Supplementation of coenzyme Q10 is not suitable for everyone, especially for middle-aged and elderly people,
blind supplementation may not only fail to achieve the expected health effects, but also may bring unnecessary side effects,
a scientific and reasonable supplement plan is particularly important.
Balanced diet, appropriate exercise, good rest and rest habits,
these seemingly simple daily behaviors are actually the most basic and effective way to maintain the balance of coenzyme Q10 in our body.
Through active adjustment in life, it can not only enhance the production of coenzyme Q10 in the body,
but also promote its effective use, thus providing double protection for our health.
Reference material
- Journal of Neonatology, Liao Qi. Coenzyme Q_(10) combined with Salvia miltiorrhiza in the treatment of myocardial damage after neonatal asphyxia [J].2004,19(3)
- Gao Xiaofeng, Luo Yinggang, Guan Jiafa. Research progress on production of Coenzyme Q10 by microbial fermentation [J],2006,18(5)
- 3, Chinese Journal of senile cardio-cerebrovascular diseases. Advances in the treatment of heart failure with Coenzyme Q10, 2019,26(05)
- 4, Chang Yiyong. Family Medicine (second half of the month), Coenzyme Q10 combined treatment of coronary heart disease and complications [J]. 2023
- Wang Shuying, Shao Zhongfu. Biological function and clinical application of Coenzyme Q10 [J]. Journal of Qiqihar Medical College,1994,15(1)